Australian Dollar Forecasts for 2024

The Australian dollar’s (AUD) performance will be driven by a diverse range of factors in 2024.
The Australian dollar (AUD) is one of the most heavily traded currencies in the world, with its value influencing the decisions of individuals, businesses and government.
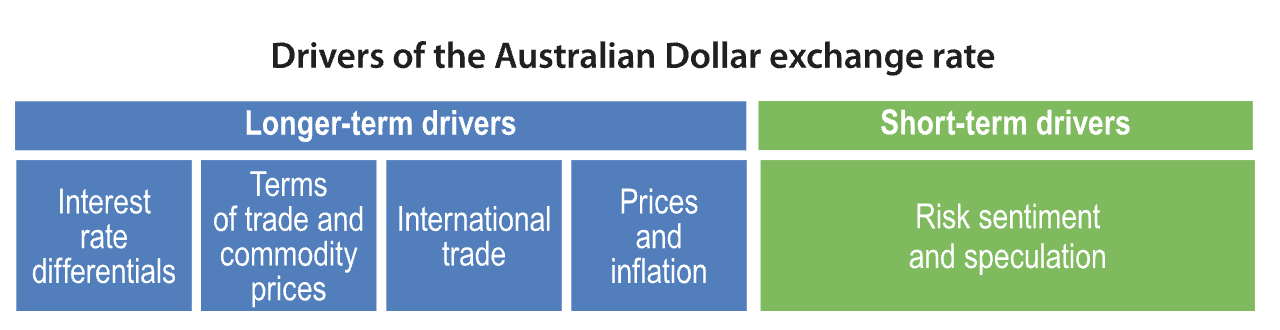
Exchange rates are notoriously volatile with the AUD’s performance driven by factors including Australia’s interest rates, inflation, terms of trade, and risk sentiment.
While the value of the AUD is typically measured against the US dollar (USD) – which is the world's principal reserve currency – the AUD’s value actually moves differently depending on the currency.
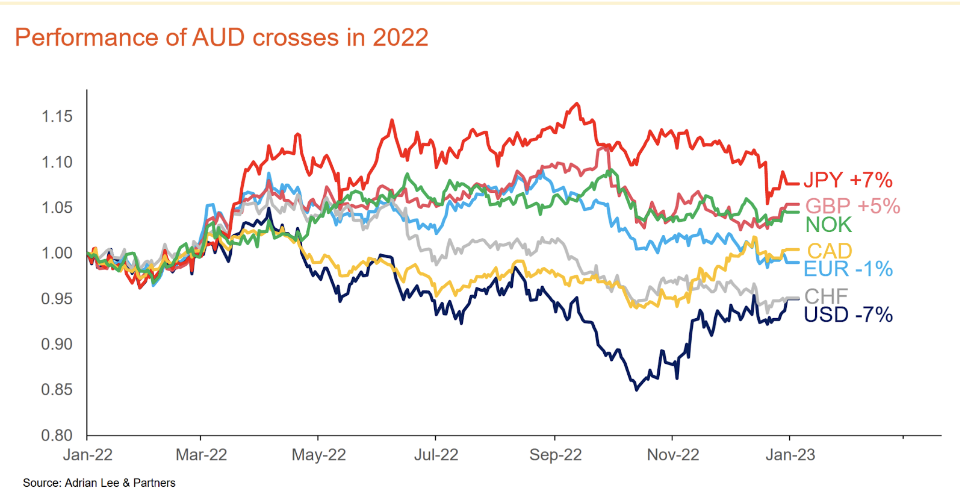
For example, in 2022, the AUD lost 7 per cent against the USD but gained 7 per cent against Japan’s Yen, as shown in the graph.
This creates specific geographic risk that needs to be managed by travellers, global investors, and companies that trade overseas.
Superannuation funds, for example, typically hedge 25-30 per cent of their international equity portfolios, according to consultant Frontier Advisors, which helps manage the risk of a potential fall in the value of the AUD
Is the Australian dollar likely to go up or down?
Leading into 2024, most bank forecasts are predicting the Australian dollar to rise. It will be influenced by interest rates, commodity prices and risk appetite.
What drives the short-term value of the AUD?
Currencies are traded continuously and can dramatically move in response to new economic data over the short-term. These moves can severely impact tourists who have planned holidays in advance, only to be hit by an unexpected currency devaluation.
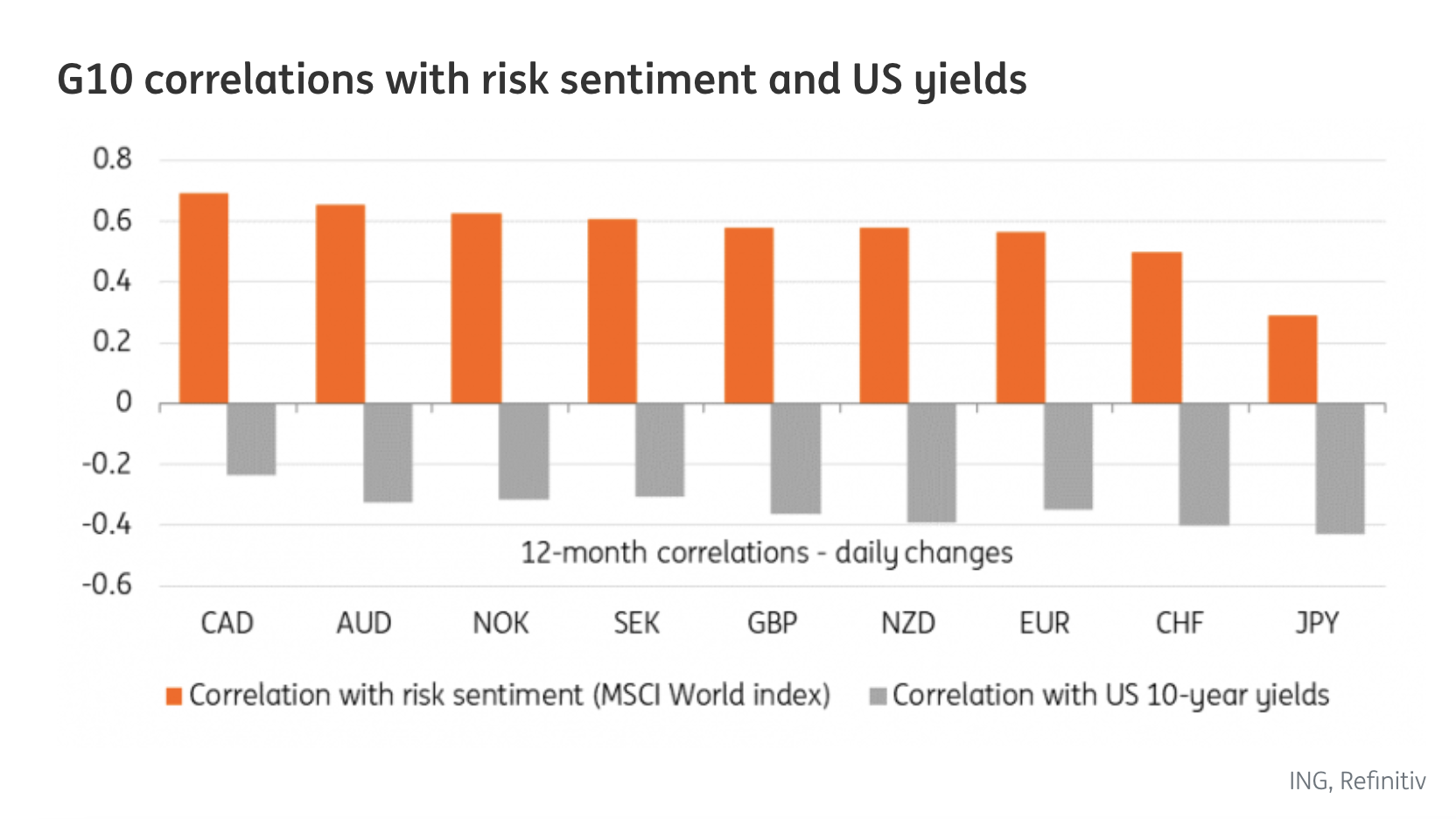
Short-term drivers can be as subtle as a change in risk sentiment or speculation about future currency movements. The AUD tends to appreciate when global equity markets rise. The AUD is particularly sensitive to perceptions of equity risk, according to ING.
“Much of the outlook for an ultra-sensitive currency to global risk sentiment like AUD remains strictly tied to external developments,” ING analysts said. “As shown below, AUD/USD is the second most sensitive USD-cross in G10 to swings in global equity-related risk sentiment, while its correlation with US back-end rates is not higher than other cyclical currencies like NZD, EUR and GBP.”
What drives the long-term value of the AUD?
Interest rate differentials – the difference between Australian interest rates and those in other countries such as the US, Europe and Japan – are a key driver of exchange rates.
For example, if the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) raises interest rates it will make Australian interest-bearing assets more attractive to local and foreign investors, driving up demand for AUD.
Another factor is Australia’s terms of trade, which measures the ratio of export prices to import prices.
When the terms of trade increase (Australia is exporting more than it is importing), it tends to strengthen the AUD. Trade volumes also play a similar role in changing demand for the AUD.
Australia’s main exports are commodities, such as iron ore and coal, which is why the AUD is sometimes referred to as a commodity currency.
It was a commodities boom driven by surging demand from China that pushed the AUD to a record high of US$1.10 in 2011. More recent concern over the state of China’s economy has also been a key reason the AUD fell to around US63c in October 2023.
Another factor is relative prices in countries. Over the long-term, exchange rates tend to adjust so that the cost of an identical basket of goods and services is the same in any two countries.
AUD to USD
AUD to USD
AUD to USD Chart
Where is the AUD headed in 2024 against the major currencies?
A key driver of the AUD is the interest rate differential level between Australia’s official interest rates and those in other countries.
The RBA was slow to begin raising rates in May 2022 compared to many other central banks, which also ultimately raised rates higher than in Australia.
This has placed downward pressure on the AUD compared to the US dollar (USD), Euro (EUR), and British Pound (GBP).
However, analysts expect the interest rate differential to contract in 2024 as central banks around the world get rising inflation back under control. Countries such as the US, European Union, and United Kingdom are expected to cut rates sooner than Australia.
This will generally help support the value of the AUD against the USD, EUR and GBP in 2024.


Over the ditch
New Zealand is a similar export-oriented economy that is linked to China’s fortunes. Analysts expect the AUD to be relatively flat in 2024 against the NZ dollar (NZD).
However, there remains significant uncertainty in the outlook.
Rising inflation has historically proven difficult for central banks to bring back under control. Several central bank interest rate decisions have surprised markets, causing large changes in exchange rates.
In Japan
Japan has been an outlier among central banks, which has weakened the Yen (JP¥) in recent times. While interest rates have quickly climbed in most developed nations, Japan’s interest rates remain in negative territory.
Analysts expect Japan’s interest rates to finally start increasing in 2024, which means the AUD would likely decline slightly against the JP¥.
However, the Bank of Japan has consistently proven slow to change direction over many years, which adds another level of uncertainty.